- 07/06/2025
- Dr. Samrat Jankar
- 0 Comments
- Blog
Understanding Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Rising Digestive Disorder
In recent years, the incidence of Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) has increased dramatically, drawing attention from gastroenterologists and patients alike. What was once considered a rare condition is now identified as a common cause of swallowing difficulties and food impaction, especially in younger individuals.
At Kaizen Gastro Care, Pune, the best esophagitis specialist in Pune Dr. Samrat Jankar highlights early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans for EoE to control long-term complications. This blog explores what EoE is, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and effective management strategies.
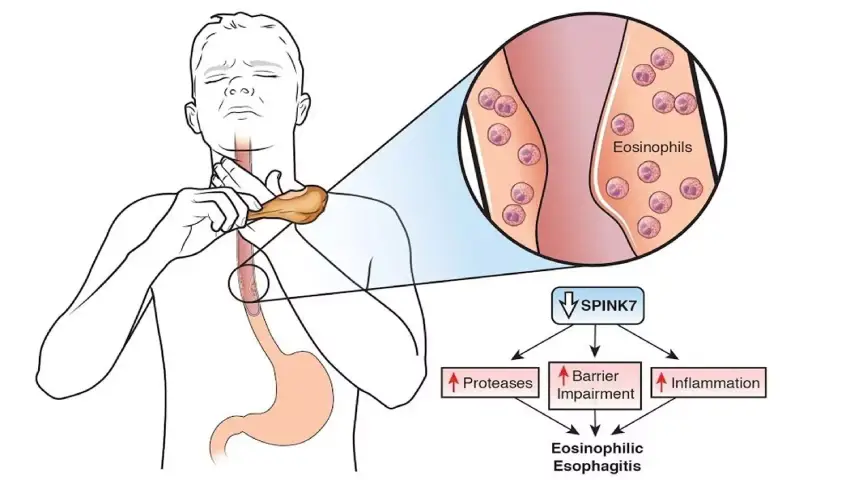
What is Eosinophilic Esophagitis?
Eosinophilic Esophagitis is a chronic inflammatory condition of the esophagus, mainly driven by an immune response. It is indicated by the presence of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, in the lining of the esophagus. Normally, eosinophils are not found in the esophagus, so their presence indicates an abnormal allergic or inflammatory reaction—often triggered by food allergens or environmental allergens.
Over time, the inflammation can lead to esophageal narrowing, fibrosis (scarring), and difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia).
Why is EoE Considered a Rising Digestive Disorder?
In the past two decades, awareness of EoE has grown rapidly among healthcare professionals. Previously misdiagnosed as GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease), improved diagnostic techniques such as upper endoscopy and esophageal biopsy have helped in accurately identifying EoE cases. Studies suggest that 1 in every 2,000 people may be affected by EoE, and the numbers are increasing, particularly in young males and children.
This rise may be attributed to:
- Increased environmental and food allergens
- Genetic predisposition
- Lifestyle and dietary changes
- Better awareness and screening
Symptoms of Eosinophilic Esophagitis:
Eosinophilic Esophagitis symptoms may vary depending on the patient’s age and the severity of the inflammation. Common signs include:
In Adults:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
- Food impaction (food getting stuck in the esophagus)
- Chest pain that is not cardiac in origin
- Heartburn or acid reflux not responding to medication
- Unexplained weight loss
In Children:
- Feeding difficulties
- Vomiting or regurgitation
- Poor growth or failure to thrive
- Stomach pain or irritability after eating
Over time, if untreated, EoE can cause permanent esophageal narrowing or strictures, making eating painful and difficult.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause of Eosinophilic Esophagitis is still under investigation, but it’s widely considered to be an allergic reaction to specific foods or airborne allergens.
Common triggers include:
- Milk
- Wheat
- Eggs
- Soy
- Peanuts
- Shellfish
- Pollen and dust mites (environmental allergens)
Other contributing factors:
- Genetics: A family history of EoE, asthma, or allergic conditions increases risk.
- Immune dysfunction: EoE is often associated with other allergic diseases like eczema or seasonal allergies.
- Male gender: EoE is more prevalent in males than females.
- Age: It often starts in childhood or early adulthood.
When to See a Gastroenterologist?
If you or your child are experiencing persistent symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, frequent heartburn, or food sticking in the throat, it’s time to consult a specialist. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications and enhance quality of life.
At Kaizen Gastro Care, Dr. Samrat Jankar uses a detailed diagnostic approach to identify EoE and rule out other conditions like GERD or infections.
Diagnostic Approach to EoE:
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
- Clinical History & Symptoms: Evaluation of symptoms like dysphagia, food intolerance, or history of allergies.
- Upper Endoscopy (Esophagogastroduodenoscopy – EGD): A flexible tube is inserted to visualize the esophagus. EoE may show white plaques, linear furrows, or rings (trachealization of the esophagus).
- Esophageal Biopsy: Multiple tissue samples are taken during endoscopy and examined under a microscope. The hallmark of EoE is ≥15 eosinophils per high-power field.
- Allergy Testing: Though not always conclusive, testing for food or environmental allergens may be useful, especially in children.
Treatment Options for Eosinophilic Esophagitis:
The goal of treatment is to lower inflammation, manage symptoms, and prevent esophageal damage. Dr. Samrat Jankar provides a personalized treatment approach based on patient age, severity, and allergen sensitivity.
Dietary Management:
- Elimination Diets: Removing common food allergens from the diet (milk, soy, wheat, eggs, nuts, seafood).
- Elemental Diets: Liquid formulas that eliminate allergens; often used in children.
- Targeted Elimination: Guided by allergy testing or food trials.
Medications:
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Help some patients by lowering acid and inflammation.
- Topical Steroids: Swallowed corticosteroids (e.g., budesonide or fluticasone) reduce eosinophilic inflammation without systemic effects.
Esophageal Dilation:
- For patients with strictures or significant narrowing, endoscopic dilation may be needed to relieve dysphagia.
Living with EoE: Lifestyle Tips:
Managing EoE is a long-term commitment that involves dietary changes, medication adherence, and regular monitoring. Here are some helpful tips:
- Work with a dietitian to provide nutritional adequacy while on elimination diets.
- Chew food thoroughly and eat slowly to control food impaction.
- Stay hydrated during meals to relieve swallowing.
- Maintain follow-up visits with your gastroenterologist to observe progress and adjust treatment.
Conclusion:
Eosinophilic Esophagitis is more than just a food allergy or heartburn. It’s a chronic immune condition that requires careful evaluation and a personalized treatment approach. Thanks to growing awareness and advanced diagnostic tools, patients today can receive effective care and lead a normal life.
If you’re experiencing unexplained swallowing issues or persistent digestive symptoms, don’t delay. Get evaluated by an expert and take the first step toward recovery.
